DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 2 Configuring BGP IP VPN
2-43
z If CSC-PE and CSC-CE are in different autonomous systems, then EBGP is generally used
to exchange internal routes, and EBGP IPv4 route/label distribution capability is also
enabled to exchange internal routes and label binding information.
Typical application scenarios
The Second Carrier can be ordinary ISP or MPLS service provider. Depending on the type of
Second Carrier network and the services provided by the Second Carrier for users, there are
following typical application scenarios:
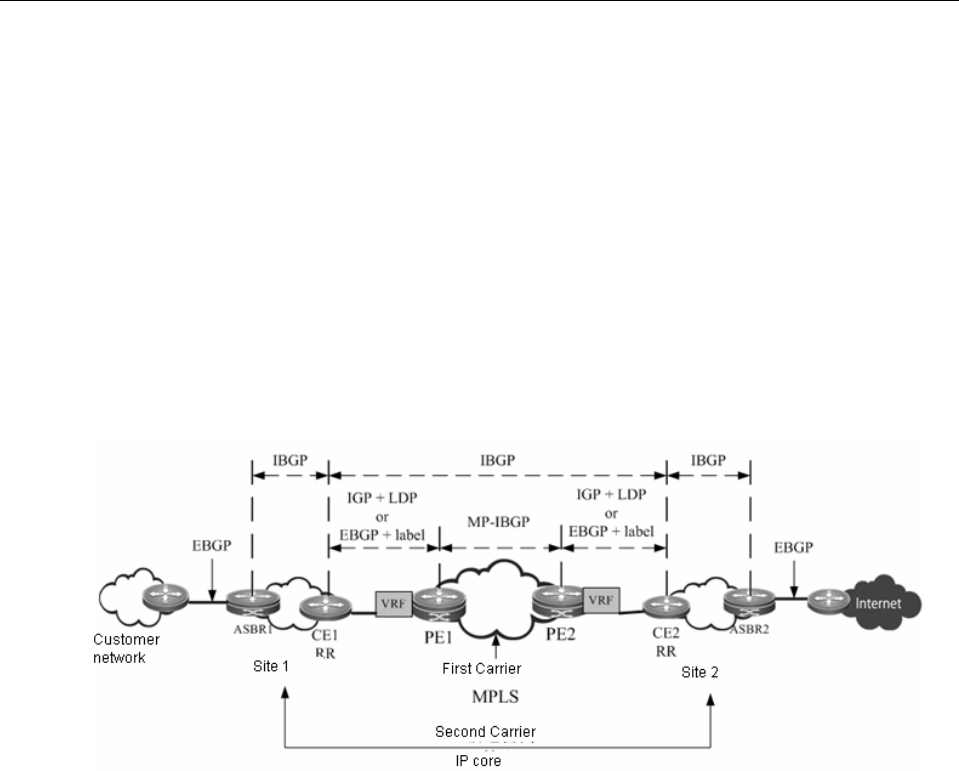
Scenario I: IP core second-level ISP
Fig 13 Scenario I: IP core second-level ISP
As shown in Fig 13, the Second Carrier is the IP core and provides network access service for
users. Adjacencies are established between ASBR1, ASBR2, CE1 and CE2 to exchange
external routes. CE1 and CE2 are Route Reflectors (RR) to reflect external routes between
different sites. The Internet-access traffic of user flows from ASBR1 into the network of Second
Carrier and then flows out of the Second Carrier network from ASBR2. When the traffic flows
from CE1 to CE2, the traffic is forwarded in the VPN LSP tunnel.
Scenario II: MPLS core second-level ISP


















