DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 6 BGP
Configuration
6-40
investment on network equipment.
6.25.2 Working principle of BGP MCE
With BGP/MPLS VPN, data of private networks can be transmitted in the public
network securely through tunnels. However, in a typical BGP/MPLS VPN network,
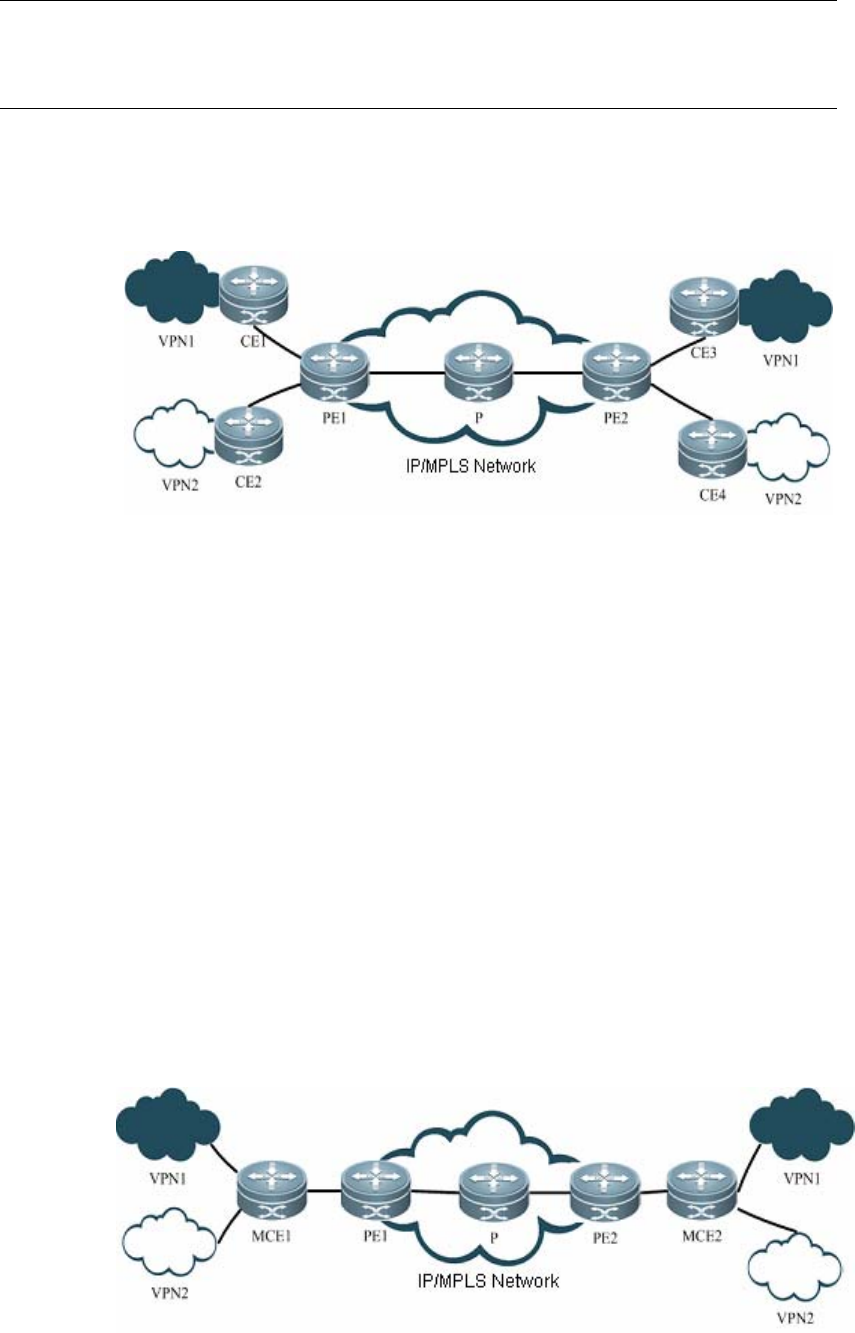
each VPN is connected to the PE through a CE, as shown in Figure 15:
Fig 15 BGP/MPLS VPN network
With the users' increasing demand for service segmentation and security, a
private network may be divided into multiple VPNs, and the users of different
VPNs are usually isolated from each other. In such a circumstance, equipment
investment and maintenance cost may increase by assigning a CE for each of the
VPNs, while data security cannot be guaranteed by sharing one CE and using the
same routing entry among multiple VPNs. MCE can well address the
contradiction between data security and network cost. By binding the VLAN
interfaces of CE device to the VPNs in a network, you can create and maintain a
routing table for each of the VPNs (Multi-VRF). In this way, packets of different
VPNs in the private network can be isolated. Moreover, with the cooperation of
the PE, the routes of each VPN can be advertised to the corresponding remote
PE properly, so that packets of each VPN can be transmitted securely through the
public network.
The following example shows how MCE maintains routing entries of multiple
VPNs and how the MCE exchanges VPN routes with PEs.
Fig 4 MCE functional diagram


















