DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 8 DHCPv6 Client Configuration
8-3
Stateless DHCPv6 auto-configuration. During the auto-configuration of network
nodes, the address configuration is independent from parameter configuration,
and each corresponding configuration can be acquired via the DHCP protocol,
which means network nodes can acquire other non-address parameters from
the DHCPv6 server. Compared with the allocation method used in DHCPv4, this
is a critical change. Relevant information is detailed in RFC3736.
Prefix delegation. Apart from IPv6 address, network prefix can also be delegated
via DHCPv6. This also accredits to the definition of IA in DHCPv6. A prefix can
be delegated to the client in the form of address (or time parameter, etc) only by
expanding the type of IA. Such a new type of IA is called IA_PD (Identity
Association for Prefix Delegation), and it is detailed in RFC3633.
8.1.1 Introduction to the
DHCPv6 Server
The DHCPv6 server realizes the allocation of IAPD and IANA. The allocation of IANA
refers to the automatic allocation of IPv6 address to the DHCP client, which is similar
to DHCPv4. The allocation of IAPD allows flexible site-level auto-configuration to
control the address range of sites. Terminal devices (such as PC) can realize
auto-configuration of address via stateless auto-configuration or stateful
auto-configuration.
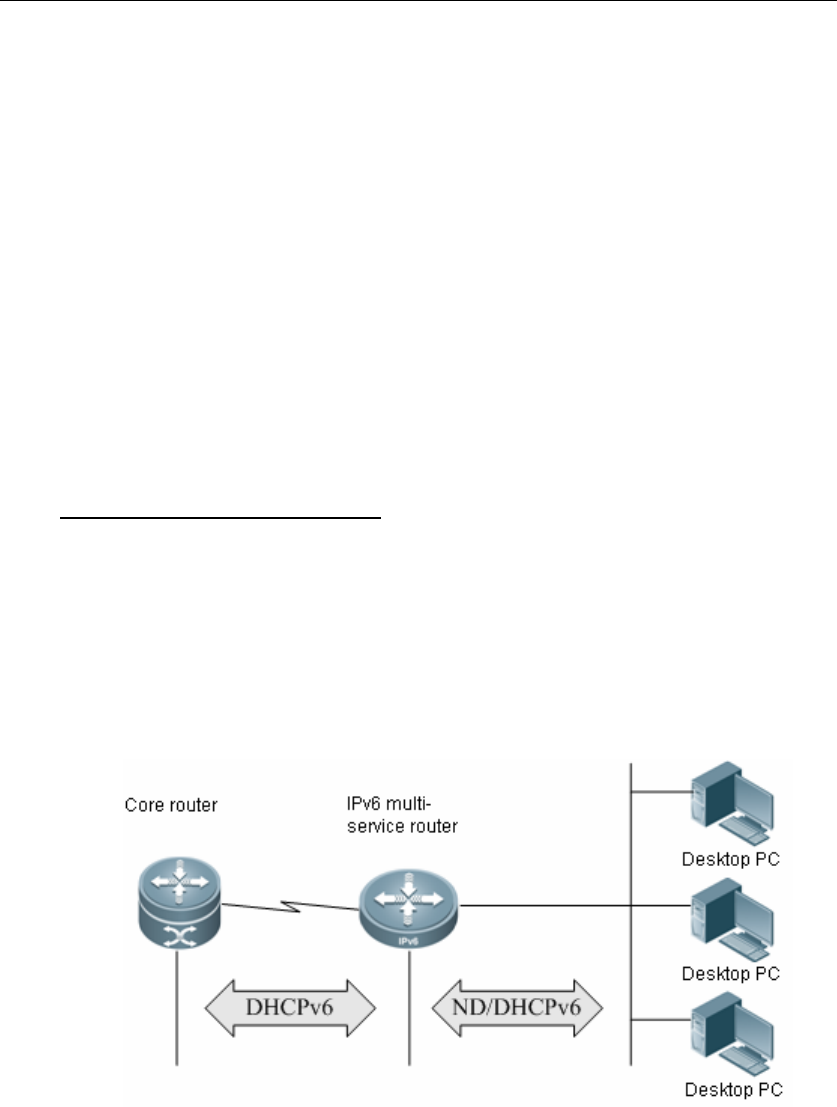
Fig 2 Prefix-based DHCPv6 application
The above figure illustrates the application of prefix-based DHCPv6 in IPv6 network.
Core router runs prefix delegation (PD) based DHCPv6 server.
IPv6 multi-service router runs the DHCPv6 client on the interface connecting to
the core router, acquiring prefix space from the core router and storing it in the
global prefix pool of IPv6.


















