DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 3 MPLS QOS
Configuration
3-2
modes as WRR (Weighted Round Robin), DRR and SP can be applied to IP
packets in order to achieve weighted random early detection (WRED), traffic
monitoring and traffic shaping. We can use the same features according to EXP
bits while implementing MPLS QoS.
3.1.2 <MPLS QoS Concept
and Terminology>
This section defines MPLS QoS related terms.
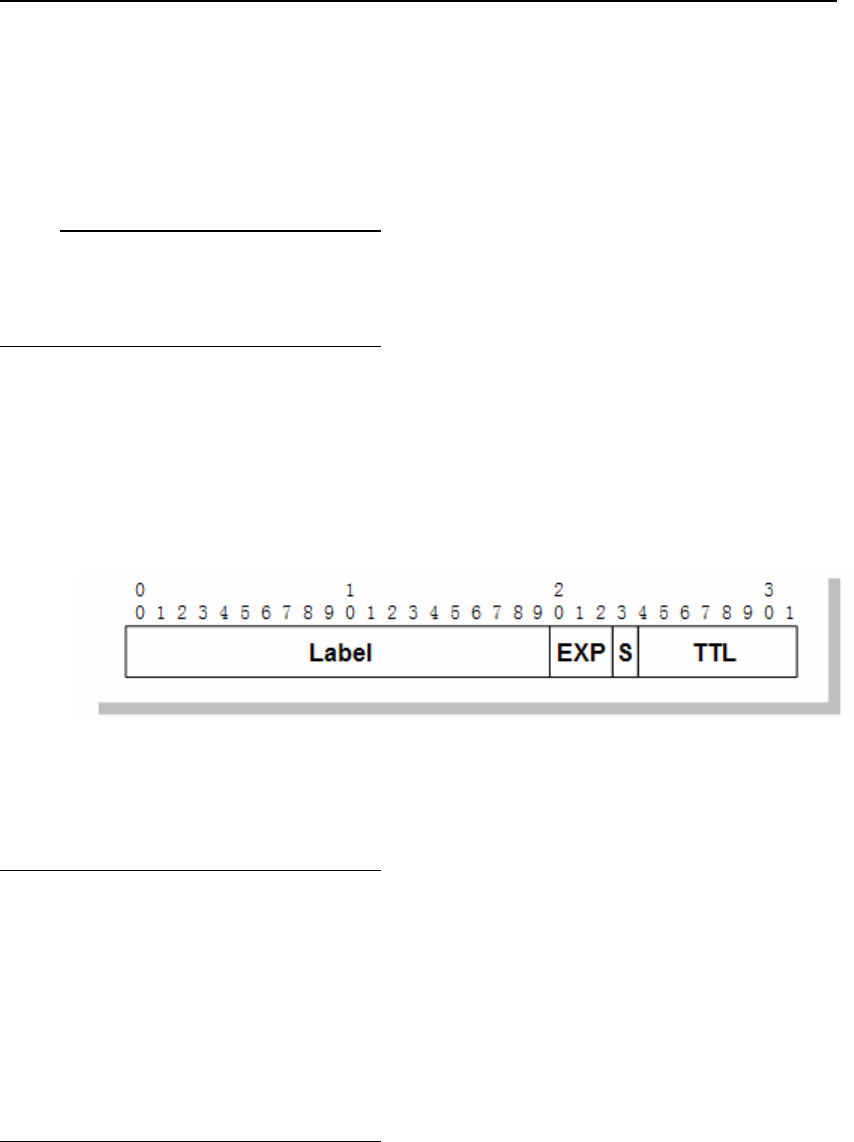
3.1.2.1 <EXP>
EXP bits refer to the 20th to 22nd bits in MPLS label. These three labels are
called experimental (EXP) bits, and are currently exclusively used for Quality of
Service (QoS). The position of EXP field in MPLS label is shown in Fig 2. Like
IP packets which can be classified and marked as per IP precedence and
DSCP bits, in MPLS network, MPLS packets can also be classified and marked
as per the EXP bits.
Fig 2 MPLS label architecture
3.1.2.2 <PHB>
Per-hop Behavior (PHB) defines how the router will handle packets while
forwarding packets. "Per-hop" means that the behavior as mentioned here
involves only the behavior of router-forwarding hop, and the behavior of
next-hop router has nothing to do with this router. Generally, forwarding of IP
packets based on IP Precedence/DSCP is called IP PHB, and forwarding of
MPLS packets based on EXP is called MPLS PHB.
3.1.2.3 <E-LSP>
A LSP with PHB determined by EXP bits. During the forwarding process, LSP
determines the forwarding path, but EXP bits determine the scheduling and
discarding priority on each hop of LSR. Therefore, a single LSP can support up
to eight classes of traffic with different PHBs (the range of 3-bit EXP field is 0-7),
which are differentiated as per the EXP bits in MPLS header.


















