DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 2 Configuring BGP IP VPN
2-26
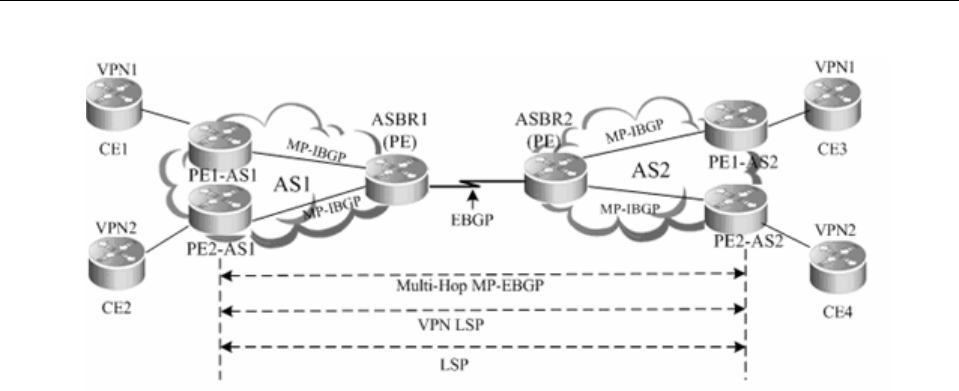
Figure 10 Multi-hope MP-EBGP
Characteristics and limitations
In the multi-hop MP-EBGP mode, only PEs rather than ASBRs are required to store VPN
information. This incurs complex configurations. This scheme is applicable to networks to be
deployed with inter-AS VPN services in a large scale.
In terms of implementation principle, OptionC is further classified into two modes:
Enable label exchanging of IPv4 routes only between EBGP neighbors.
Enable label exchanging of IPv4 routes between EBGP and IBGP neighbors.
To facilitate scale expansion in OptionC, each AS is generally deployed with a route reflector
(RR). The RRs of two ASs set up multi-hop MP-EBGP sessions to exchange VPN routes.
Judged from deployment, OptionC can be referred to as the scheme of "Multi-Hop MP-EBGP
Session Setup Between RRs".
The following describes the configuration procedures of these solutions.
Scheme 1: Enabling label exchanging of IPv4 routes only Between EBGP Neighbors
In this scheme, the IGP (such as OSPF or RIP) that runs on an ASBR is required to
redistribute BGP routes so that each device in the AS can have routes to the PE in another
AS. In the AS, you can use the LDP to set up an LSP for label distribution with the PE in
another PS. On the directly connected ASBRs of the two ASs, enable label exchanging of
IPv4 routes. In this manner, BGP serves as the MPLS signaling to assign labels to the PE in
another AS and set up an inter-AS LSP.
The configuration procedure is as follows:
Configuring Route Exchanging Between PEs and CEs


















