DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 1 MPLS Configuration
1-3
4. Operations to the label stack of data packets, including:
a) Replacing the label of the label stack top with a new label
b) Popping out the label of the stack top
c) Adding one or more labels
d) Replacing the label of the label stack top with a new label and adding one or more
new labels
Incoming Label Map (ILM)
The ILM table is a label forwarding table that maps each incoming label to a series of
NHLFEs (multiple NHLFEs indicate multiple paths). The ILM is applied when an LSR
receives and forwards MPLS packets with labels.
FEC-to-NHLFE (FTN)
Different from ILM, the FTN maps each FEC to a series of NHLFEs (multiple NHLFEs
indicate multiple paths). The FTN table is used when an LER receives and forwards packets
without labels and is required to encapsulate labels to the packets before forwarding them.
1.1.2 Label
A label is a short identifier with fixed length and of local significance. The label is distributed and
transmitted only between two adjacent LSRs. As a result, it is valid only between the two LSRs.
One label identifies one FEC. When arriving at the MPLS ingress, packets are classified into
different FECs according to certain rules. Based on the FECs, the packets are encapsulated with
different labels and then forwarded on the MPLS network based on the labels.
1.1.2.1 Label Structure
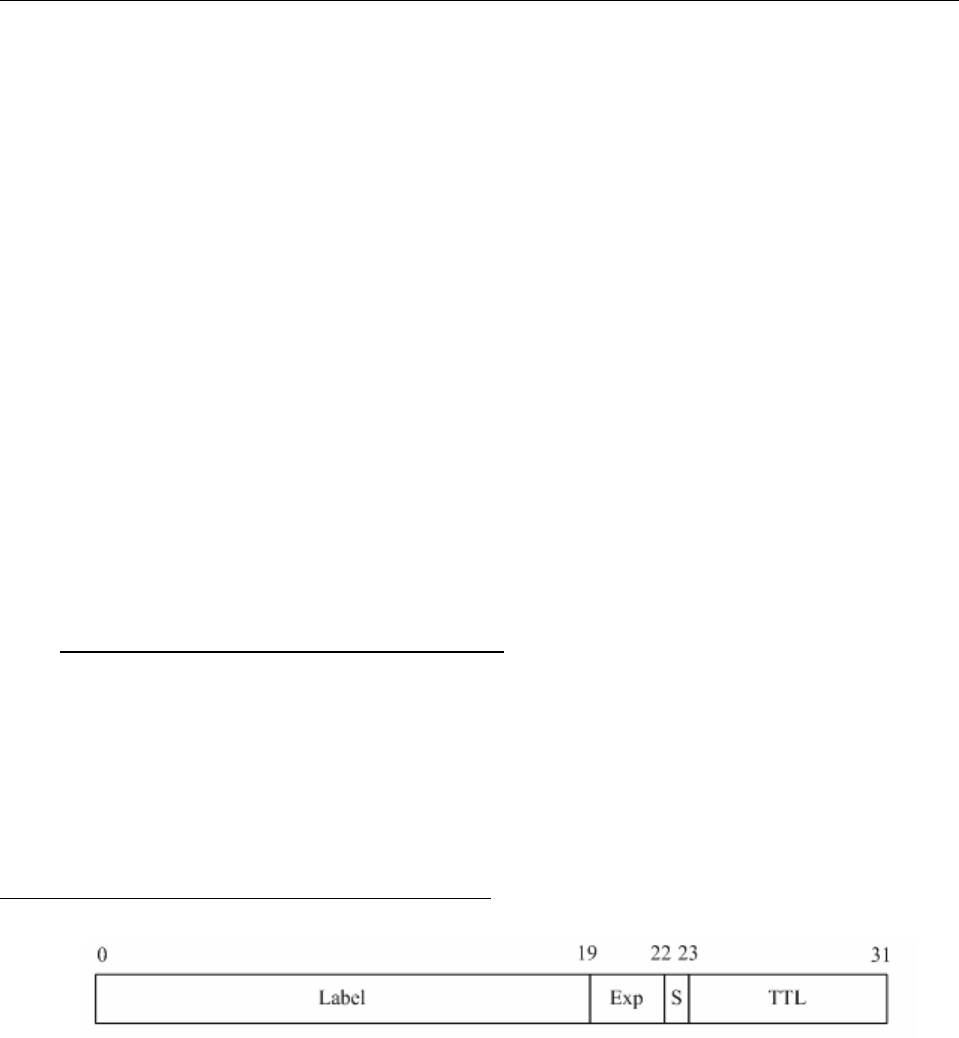
Figure 1 Encoding structure of an MPLS label
As shown in the preceding figure, a label consists of four fields. The following introduces the four
fields separately:
¾ Label field
The label field is used to save the label that is 20 bits long. The label value is an index to the
forwarding table of labels. The IETF defines 0 to 15 as reserved labels and predefines the
meanings of these label values:


















