DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 2 MAC Address Configuration
2-4
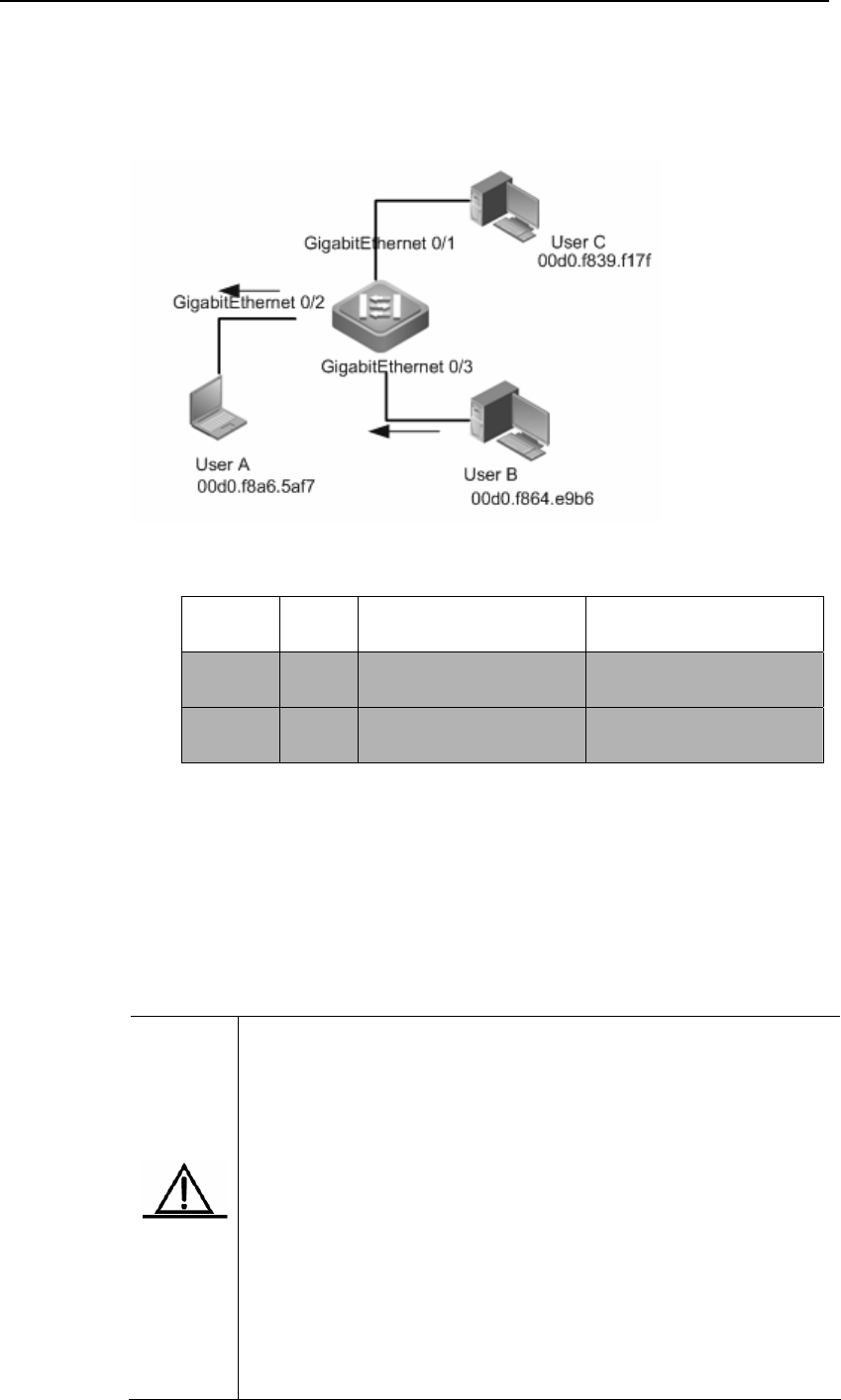
table. Therefore, the packets are forwarded to interface GigabitEthernet 0/2 in
the unicast form and the switch learns the MAC address for UserB at the same
time. The difference from the step one is that UserC can not receive the packets
sent from UserB to UserA.
Figure4 Dynamic Address Learn (Step 2)
Status VLAN MAC address Interface
Dynamic 1 00d0.f8a6.5af7 GigabitEthernet 0/2
Dynamic 1 00d0.f8a4.e9b6 GigabitEthernet 0/3
Figure5 MAC Address Table 2
After the communication between UserA and UserB, the switch learns the
source MAC addresses for UserA and UserB. The mutual packets between
UserA and UserB are forwarded in the unicast form and UserC can not receive
them again.
Caution
In the stack system, the address tables of each member device
are asynchronous. For example:
Suppose the device A and device B stack and the device A is the
host, send the broadcast packets to the device A, the port
receiving the frames on the device A will learn the MAC1 address,
which will be recorded in the address table. Since the packets are
broadcasted to the device B through the stack port, the stack port
on the device B will also learn this MAC1 address but not record it
in the address table.
Removing the MAC address learned from the frame-receiving port
on the device A, the MAC1 address in the address table will also
be removed. However, the stack port of the device B still learn this


















