DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 9 DHCP Snooping Configuration
9-3
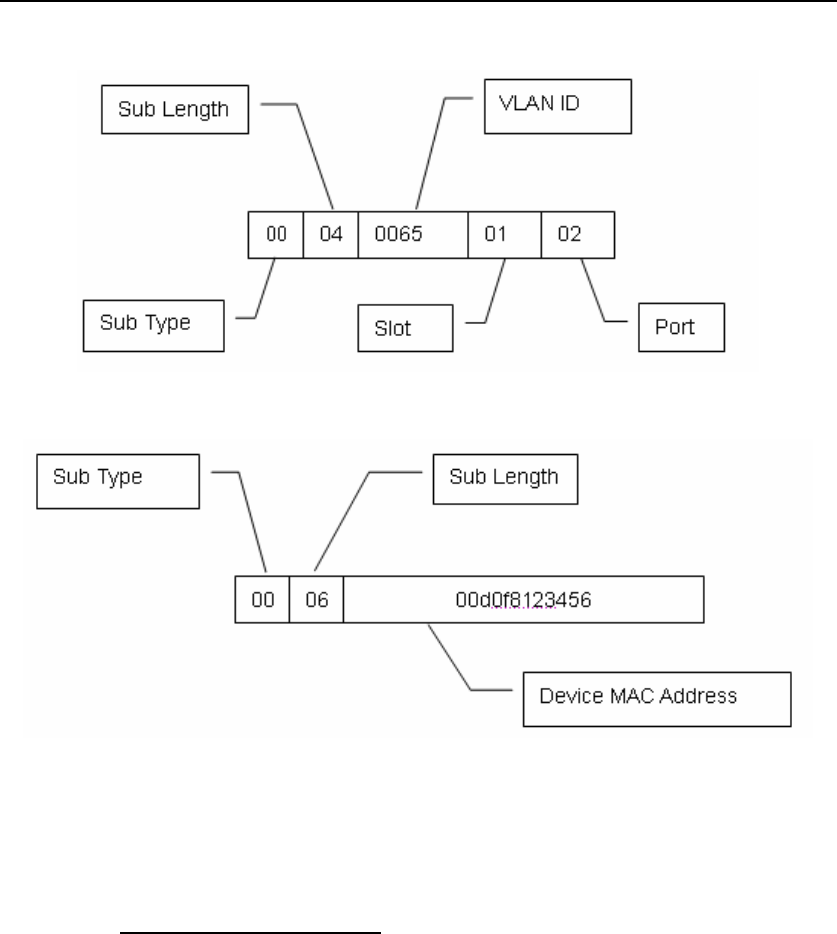
Agent Circuit ID
Agent Remote ID
9.1.4 DHCP
Snooping
Related
Security
Functions
In the DHCP-enabled network, the general problem facing administrator is that some users
use private IP addresses rathe than dynamically obtaining IP addresses. As a result, some
users using dynamic IP addresses cannot access the network, making network application
more complex. In dynamic DHCP binding mode, the device records how legal users obtain IP
addresses during the course of DHCP Snooping for security purpose. There are three ways of
security control. The first one is to enable address binding for legal users in conjunction with
the IP Source Guard function; the second one is to use DAI to check the validity of users by
controlling ARP; the third one is to bind the ARP message of legal users in conjunction with the
ARP Check function. It should be noted that given the limit of hardware entries in the first
mode, the switch supports limited DHCP users. Where there are too many users on the switch,
some legal users may not access the network for they cannot add hardware entries. In
addition, the second method will influece the performance of the switch at a large extent,
because all ARP messages are forwarded and processed by CPU.
For the details on the priorities of DHCP Snooping and other security functions, refer to Port


















